Anal Fistula and Treatment Options: Your Questions Answered
October 17, 2017Achalasia
October 23, 2017
Colorectal cancer is cancer affecting the large intestine and rectum. There has been a rapid increase in colorectal cancer in India, and this can be attributed to two factors:
- Increasing life expectancy
- Following the western lifestyle
Most cases occur above the age of 50. It is true that if detected early, then colorectal cancer can be cured.
How does colorectal cancer develop?
Contrary to belief, it takes years to develop colorectal cancer. It develops from the inner lining of the bowel (mucosa). Initially, it forms a polyp, which over time turns into cancer. The tumour then starts to invade through different layers of the bowel wall and into the lymph nodes near it. If undetected, it can eventually spread to different parts of the body.
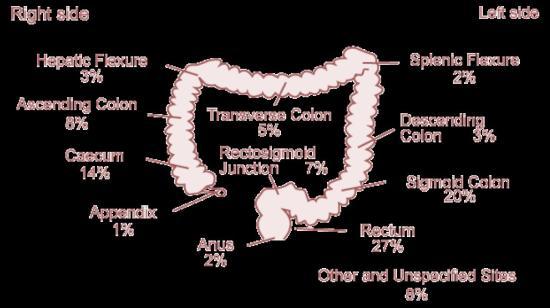
Most of these cancers are on the left side (see picture).
Can polyp be treated?
Yes. Most polyps do not contain cancer cells. Removal of polyp will be sufficient to prevent the cancer from developing.
In some cases, even after removing the polyp, cancer cells may be found. If the cancer cells have spread to the colon, then further surgery is advised if necessary.
What are the risk factors for colorectal cancer?
- Increases with age
- Western lifestyle
- Genetic factor (first-degree relative having colorectal cancer)
- Long-term inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s or Ulcerative colitis)
What reduces colorectal cancer?
- Hormonal replacement therapy for women
- Vegetarian diet
What are the symptoms of colorectal cancer?
Initially, there might be no symptoms or very few symptoms. The symptoms would increase when the cancer grows in size. The symptoms include:
- Change in bowel habit either to constipation or to passing too many times
- Sensation of incomplete emptying after passing motion
- Blood mixed with the stool
- Passing mucus with stool
- A sensation of fullness after eating little
- Abdominal distension
- Abdominal pain
- Weight loss
What tests are needed before surgery?
Colonoscopy and biopsy are needed to prove that it is cancer are a must unless it is an emergency.
CT scan is necessary to assess the spread inside the abdomen and chest.
MRI of pelvis should be done if the cancer is in the rectum.
What are the treatment options?
If it affects the colon, surgery is done first. After excision, the cancer is studied under a microscope. If it has spread to the lymph nodes, then chemotherapy might be needed post operation.
If it affects the rectum, in the first two stages, then surgery is done first.
If the cancer is in the third or fourth stage, then chemo radiotherapy is absolutely necessary. Operation after chemo-radiotherapy reduces the risk of recurrence from 85 percent to 5 percent (see picture).
If in Anal canal: Chemo radiotherapy is main stay of treatment.
How is the surgery done?
If the patient is fit, cancer surgery can be done safely with keyhole (laparoscopy) with 3 or 4 small incisions. Usually, the cut ends are joined using a special stapler. In certain cases, colostomy can be done if the joining is thought to be risky. The options will be discussed with risk/benefits before surgery.
Can colorectal cancer be cured?
Yes, if found in early stages. Even if it has spread to the lymph nodes, attempts can be made to cure it. In some cases, people with liver metastasis can also be cured.
